Home » Keywords: » BLDC motors
Items Tagged with 'BLDC motors'
ARTICLES
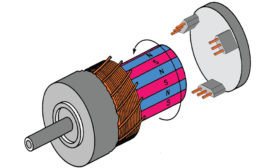
Slotless vs. Slotted Brushless DC Motor Design
Learn more about motor options.
September 2, 2015
Never miss the latest news and trends driving the manufacturing industry
Stay in the know on the latest assembly trends.
JOIN TODAY!Copyright ©2025. All Rights Reserved BNP Media.
Design, CMS, Hosting & Web Development :: ePublishing