Assembly Lines
Global Robot Density in Factories Has Doubled

Deployment of industrial robots has doubled over the past seven years.
Photo courtesy ABB Robotics
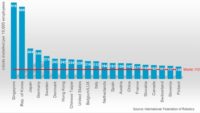
FRANKFURT—Robot adoption in factories around the world continues at high speed, according to a new report by the International Federation of Robotics (IFR). Global average robot density reached a record 162 units per 10,000 employees in 2023, more than double the number measured only seven years ago (74 units).
“Robot density serves as a barometer to track the degree of automation adoption in the manufacturing industry around the world,” says Takayuki Ito, president of IFR, who also serves as chief technical advisor at Fanuc Corp. “This year's runner-up is China, which ranks third worldwide behind Korea and Singapore, but right up with Germany and Japan.”
According to Ito, “robot density” refers to the number of operational industrial robots relative to the number of employees. “It can cover the whole manufacturing industry or just specific industrial branches,” he explains. “The number of employees serves as a measure of economic size, so the quotient of operational stock over employees puts the operational stock on a uniform base.”
North America´s robot density is 197 units per 10,000 employees, a 4 percent increase. Robot density in the United States reached 295 units in 2023. The U.S. ranks tenth in the world.
The European Union has a robot density of 219 units per 10,000 employees, an increase of 5 percent. Germany, Sweden, Denmark and Slovenia rank in the top 10.Asia has a robot density of 182 units per 10,000 persons employed in manufacturing, an 8 percent increase.
The Republic of Korea is the world’s No. 1 adopter of industrial robots with 1,012 machines per 10,000 employees. Robot density has increased by 5 percent on average each year since 2018, driven by South Korea’s automotive and electronics industry.Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!